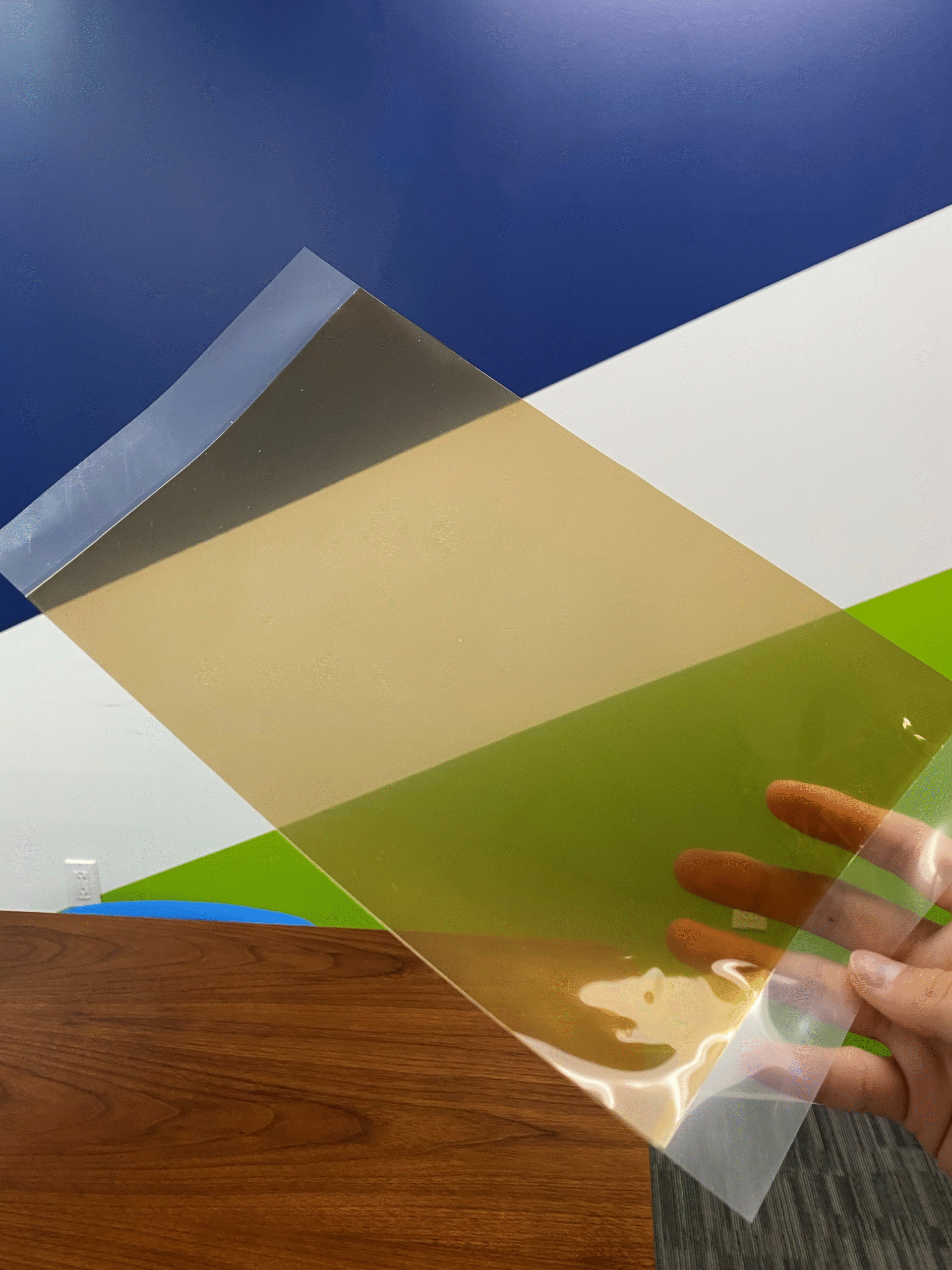
Proton exchange membranes (PEMs) and cation exchange membranes (CEMs) are special materials that selectively allow the passage of positively charged ions (cations) while blocking negatively charged ions (anions) and gases. Proton exchange membranes are specifically designed to conduct protons (H⁺ ions) and are most commonly used in fuel cells (PEMFCs), where they play a critical role in enabling electrochemical reactions that convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity. Cation exchange membranes, while similar in function, are broader in scope and can transport a variety of cations, including sodium, potassium, and calcium ions. They are widely used in applications such as water purification, electrodialysis, redox flow batteries, and other electrochemical processes where selective ion transport is essential. These membranes are integral to enabling clean energy systems and efficient chemical separations.
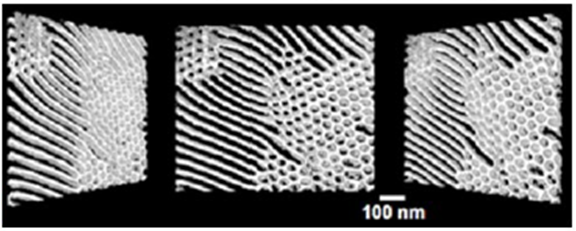
Reconstructed 3-dimensional Transmission Electron Microscopy image of pentablock ion conducting polymer. Image shows channels that run across depth (Z-axis), providing superior ionic conductivity.
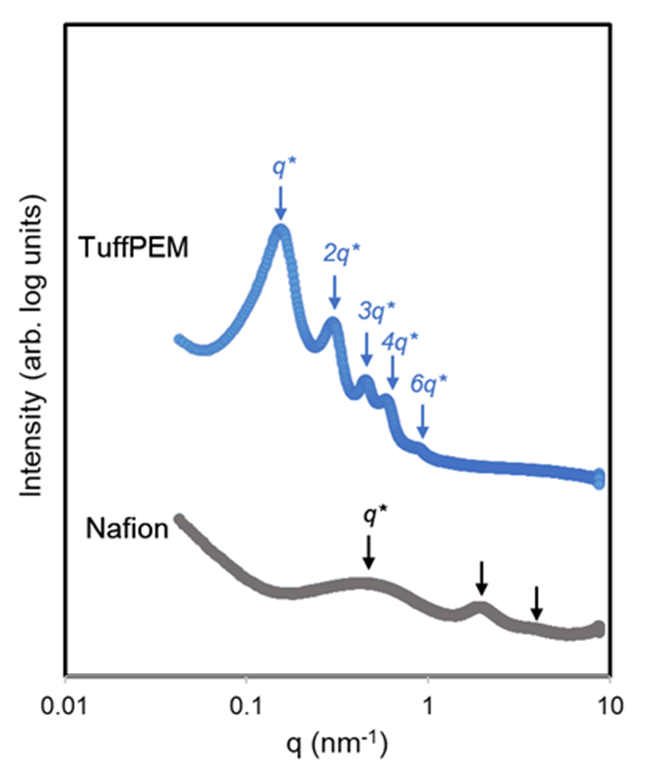
*Data from Argonne National Lab
TuffPEM Polymer Grades are available in:
* ‘xx’ relates to polymer grade and its IEC. Different configurations are available upon request, with minimum order quantity requirements.
| Polymer | Membrane Type | Membrane Thickness | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| TuffPEM 20 | Free standing | 10–50 um | Coating over lubricated PET substrate |
| TuffPEM 20 PBX5 | Free standing | 10–50 um | Coating over lubricated PET substrate |
| TuffPEM 20 CPBX5 | Composite | 15–30 GSM | Coating over microporous substrate |